01-August-2025
- China leads among importers, volumes drop y-o-y
- Ore imports by India climb up by over 18% y-o-y
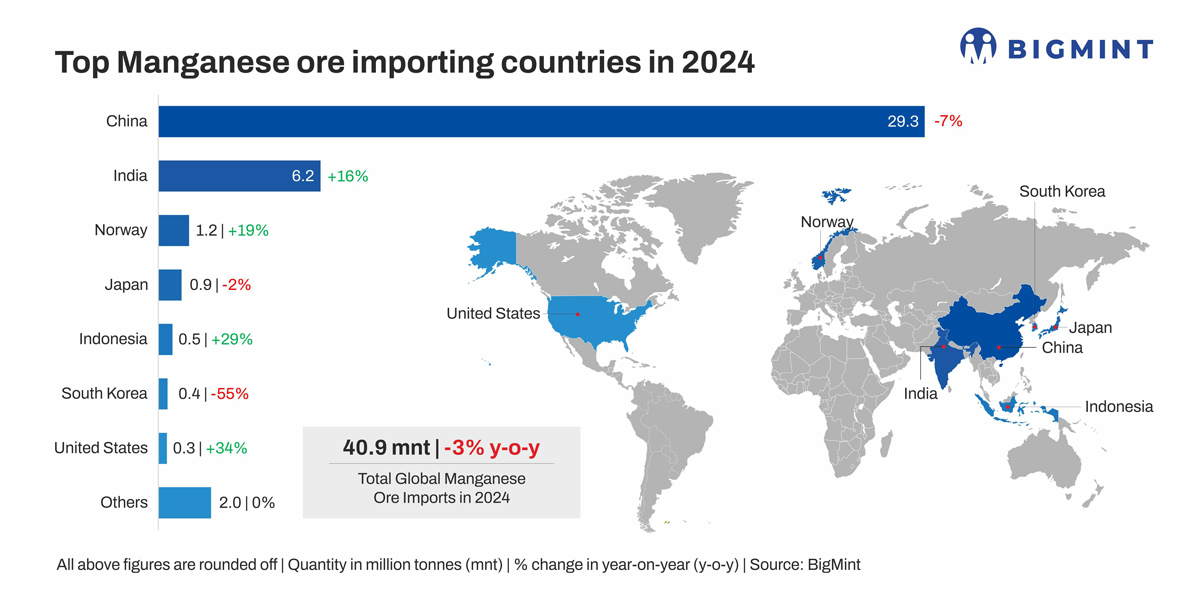
Global manganese ore imports fell by 3% y-o-y in CY'24, to 40.88 million tonnes (mnt) from 42.15 mnt in CY'23, according to data compiled by BigMint. The contraction highlights subdued demand in key importing nations amid global steel industry fluctuations and geopolitical uncertainties.
Factors driving global manganese ore trade flows
China limits intake amid tepid steel sector activity: China, the world's largest manganese ore importer, accounted for over 70% of global imports. However, in CY'24, imports declined by 6.6% y-o-y to 29.35 million tonnes (mnt) from 31.42 mnt in CY'23. The decline reflects subdued growth in crude steel output and stricter environmental regulations in key industrial regions.
In CY'24, China's crude steel production was 1.005 billion tonnes (bnt), a decrease of 1.7% compared to the previous year. Persistent challenges in the property sector also weakened construction activity, softening demand for silico manganese and ferro manganese.
Additionally, a modest rise in domestic manganese ore production to 1.19 mnt in CY'24 from 1.14 mnt in CY'23 likely contributed to reduced reliance on imports.
Supply shortages, rising alloy out boost India's imports: In contrast to the global downtrend, India's manganese ore imports rose sharply by 18.6% in CY'24 to 6.21 mnt from 5.35 mnt in CY'23. The surge was primarily driven by increased alloy production, supported by robust steel demand and limited availability of high-grade domestic ore. Moreover, aggressive stockpiling by major alloy manufacturers, amid ongoing concerns over ore supply stability, further bolstered import volumes.
India's crude steel production also registered solid growth, rising by 6% y-o-y to 150 mnt in CY24, reinforcing the upward trajectory in manganese ore demand.
Norway logs highest rise in imports amid steady alloy production: Norway recorded the highest y-o-y growth in manganese ore imports in CY'24, with volumes up by 18.6% to 1.18 mnt from 0.99 mnt in CY'23. The increase was supported by steady operations at manganese alloy smelters, underpinned by long-term contracts and energy-efficient processes, key factors enabling competitiveness despite Europe's high-cost operating environment.
Japan's imports dip as steel output slows: Japan's manganese ore imports declined by 2% y-o-y in CY'24, to 0.89 mnt from 0.91 mnt in CY'23, largely reflecting a 3% drop in crude steel output to 84.01 mnt from 87.01 mnt over the same period. The slowdown in steel production, driven by weak domestic demand and persistent industrial sluggishness, directly impacted manganese ore consumption.
Additionally, Japan's steel demand is expected to stay weak in the short term due to low buying interest, both domestically and internationally. Exports face pressure from slowing global markets, while the construction and automotive sectors remain sluggish. US trade policy uncertainty adds further risk to the outlook.
Lower exports play a pivotal role in downturn
Cyclone Megan disrupts Australian mining activity: In March 2024, Tropical Cyclone Megan severely impacted operations at South32's Gemco manganese mine in Australia, a critical global supplier of high-grade manganese ore. The resulting damage led to a four-month shutdown, which may have contributed to the decline in global manganese imports during CY'24.
In conclusion, while global manganese ore imports declined modestly in CY'24, the divergence in country-wise trends reflects varying economic conditions, domestic ore supply dynamics, and the steel sector's evolving trajectory. India and Norway stood out with strong import growth, while China's contraction shaped the overall negative trend.
Listen to industry experts and gain insights on "Balancing Manganese Alloys - Demand vs Resources" at the 5th International Ferro Alloys Conference 2025 - Navigating Trade Uncertainties: Sustainable Growth in Ferro Alloys, to be held over 2-4 September at JW Marriott, New Delhi.

